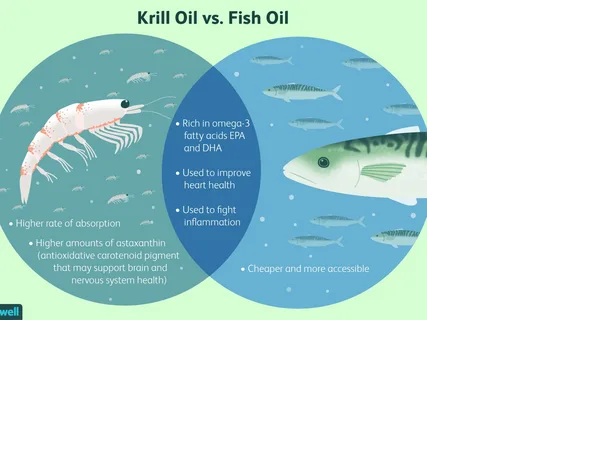
The debate between krill oil and fish oil has been ongoing as both are popular dietary supplements rich in omega-3 fatty acids. Krill oil, derived from tiny crustaceans known as krill, and fish oil, sourced from fatty fish like salmon and mackerel, offer various health benefits. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll delve into the differences between krill oil and fish oil, their respective benefits, potential drawbacks, and help you determine which one might be better suited for your health needs.
Understanding Krill Oil and Fish Oil
Krill Oil:
Krill oil is extracted from small, shrimp-like marine crustaceans called krill, which inhabit cold ocean waters. Krill are a vital part of the marine food chain and are rich in omega-3 fatty acids, primarily in the form of phospholipids, as well as astaxanthin, a potent antioxidant that gives krill its reddish color.
Fish Oil:
Fish oil is derived from the tissues of fatty fish such as salmon, mackerel, sardines, and anchovies. It contains two main types of omega-3 fatty acids: eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA) and docosahexaenoic acid (DHA). These fatty acids are essential for various bodily functions, including heart health, brain function, and reducing inflammation.
Nutrient Composition
Krill Oil:
Krill oil contains omega-3 fatty acids in the form of phospholipids, which may enhance their absorption and utilization by the body compared to the triglyceride form found in fish oil. Additionally, krill oil contains astaxanthin, a powerful antioxidant with anti-inflammatory properties.
Fish Oil:
Fish oil primarily contains omega-3 fatty acids in the triglyceride form, which may require additional processing by the body for absorption. However, fish oil supplements often provide higher concentrations of EPA and DHA compared to krill oil supplements.
Health Benefits
Krill Oil:
Heart Health: The omega-3 fatty acids in krill oil may help reduce triglyceride levels, improve cholesterol profiles, and support overall heart health.
Joint Health: Krill oil’s anti-inflammatory properties may help reduce joint pain and stiffness associated with conditions like arthritis.
Brain Function: Omega-3 fatty acids are essential for brain health and cognitive function, and krill oil may support memory, learning, and mood regulation.
Fish Oil:
Heart Health: Fish oil is well-known for its cardiovascular benefits, including reducing blood pressure, lowering triglyceride levels, and decreasing the risk of heart disease.
Brain Health: EPA and DHA found in fish oil are crucial for brain development and function, supporting memory, concentration, and mood stability.
Eye Health: DHA is a major component of the retina, and fish oil may help maintain vision and protect against age-related macular degeneration.
Bioavailability and Absorption
One of the key differences between krill oil and fish oil is their bioavailability and absorption in the body. Krill oil’s omega-3 fatty acids are bound to phospholipids, which are structurally similar to the cell membranes in the human body. This may enhance their absorption and utilization compared to the triglyceride form found in fish oil.
Sustainability and Environmental Impact
Krill Oil:
Krill are a keystone species in the marine ecosystem, serving as a primary food source for many marine animals, including whales, seals, and penguins. Overfishing of krill could disrupt marine ecosystems and threaten the survival of dependent species.
Fish Oil:
The fishing industry has raised concerns about overfishing and depletion of fish stocks, leading to environmental degradation and ecosystem imbalance. Sustainable fishing practices and responsible sourcing are essential to minimize the environmental impact of fish oil production.
Potential Drawbacks
Krill Oil:
Cost: Krill oil supplements tend to be more expensive than fish oil supplements due to the higher cost of krill harvesting and processing.
Allergies: Individuals with shellfish allergies may need to avoid krill oil supplements due to the risk of allergic reactions.
Fish Oil:
Fishy Aftertaste: Some people may experience fishy burps or aftertaste when taking fish oil supplements, especially if they have sensitive stomachs.
Mercury Contamination: Fish oil supplements derived from large, predatory fish may contain trace amounts of mercury and other environmental contaminants.
Choosing the Right Supplement
When deciding between krill oil and fish oil supplements, consider the following factors:
Personal Health Goals: Determine your specific health needs and goals, such as heart health, joint support, or cognitive function.
Bioavailability: Consider the potential benefits of krill oil’s enhanced bioavailability versus fish oil’s higher concentrations of EPA and DHA.
Sustainability: Choose supplements that are sustainably sourced and environmentally responsible to minimize the impact on marine ecosystems.
Cost and Accessibility: Evaluate the cost-effectiveness and availability of krill oil versus fish oil supplements based on your budget and preferences.
Conclusion
In conclusion, both krill oil and fish oil offer valuable health benefits due to their omega-3 fatty acid content. Krill oil may have advantages in terms of bioavailability and absorption, thanks to its phospholipid form and antioxidant properties. However, fish oil supplements provide higher concentrations of EPA and DHA, making them a popular choice for cardiovascular and brain health support.
Ultimately, the best choice between krill oil and fish oil depends on individual preferences, health needs, and considerations such as sustainability and cost. Consult with a healthcare professional or registered dietitian to determine the most suitable omega-3 supplement for your health goals and dietary preferences.
Krill oil and fish oil are two popular dietary supplements that are rich in omega-3 fatty acids, essential nutrients that offer a range of health benefits. Both krill oil and fish oil contain omega-3 fatty acids, including eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA) and docosahexaenoic acid (DHA), which are known for their anti-inflammatory properties and cardiovascular health benefits. However, there are differences between the two supplements in terms of their composition, absorption, sustainability, and potential health effects. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll explore the similarities and differences between krill oil and fish oil to help you determine which may be the better choice for your health needs.
Composition and Source
Krill Oil:
Krill oil is extracted from tiny, shrimp-like crustaceans known as Antarctic krill. Krill oil contains omega-3 fatty acids in the form of phospholipids, which are believed to enhance absorption compared to the triglyceride form found in fish oil. In addition to EPA and DHA, krill oil also contains astaxanthin, a powerful antioxidant that gives krill oil its characteristic red color.
Fish Oil:
Fish oil is derived from the tissues of fatty fish such as salmon, mackerel, sardines, and anchovies. Fish oil contains omega-3 fatty acids primarily in the form of triglycerides. While fish oil does not contain astaxanthin like krill oil, it may contain other antioxidants and beneficial compounds depending on the type of fish from which it is sourced.
Absorption and Bioavailability
One of the key differences between krill oil and fish oil is their absorption and bioavailability:
Krill Oil:
Krill oil contains omega-3 fatty acids in the form of phospholipids, which are believed to be more readily absorbed by the body compared to the triglyceride form found in fish oil. Some studies suggest that the phospholipid structure of krill oil may enhance its bioavailability, allowing for lower doses to achieve similar effects as higher doses of fish oil.
Fish Oil:
Fish oil contains omega-3 fatty acids primarily in the triglyceride form. While triglyceride-based fish oil supplements are still well-absorbed by the body, they may not be as efficiently absorbed as the phospholipid form found in krill oil. However, the bioavailability of fish oil can vary depending on factors such as the quality of the supplement and individual differences in metabolism.
Sustainability and Environmental Impact
Krill Oil:
Krill oil is sourced from Antarctic krill, which are abundant in the Southern Ocean. While krill populations are currently considered to be sustainable, concerns have been raised about the potential impact of krill harvesting on marine ecosystems and the species that depend on krill as a primary food source, such as whales, seals, and penguins.
Fish Oil:
The sustainability of fish oil depends on the source of the fish from which it is derived. Some species of fatty fish, such as salmon and sardines, are considered to be more sustainable choices due to their abundance and responsible fishing practices. However, other species of fish may be overfished or harvested using unsustainable methods, leading to concerns about the depletion of fish populations and damage to marine ecosystems.
Health Benefits
Both krill oil and fish oil offer a range of health benefits due to their omega-3 fatty acid content:
Cardiovascular Health:
Omega-3 fatty acids, particularly EPA and DHA, are known for their cardiovascular health benefits. They can help reduce triglyceride levels, lower blood pressure, improve blood vessel function, and reduce inflammation, all of which contribute to a lower risk of heart disease and stroke.
Brain Health:
Omega-3 fatty acids are essential for brain health and cognitive function. They play a crucial role in brain development and maintenance and may help reduce the risk of age-related cognitive decline, Alzheimer’s disease, and other neurological disorders.
Joint Health:
Omega-3 fatty acids have anti-inflammatory properties that may help reduce joint pain, stiffness, and inflammation associated with conditions such as arthritis and rheumatoid arthritis. Regular supplementation with krill oil or fish oil may help improve joint mobility and alleviate symptoms of joint discomfort.
Skin Health:
Omega-3 fatty acids are beneficial for skin health, helping to hydrate the skin, reduce inflammation, and protect against sun damage. Regular consumption of krill oil or fish oil may help improve skin texture, elasticity, and overall appearance.
Safety and Side Effects
Both krill oil and fish oil are generally considered safe for most people when taken as directed. However, some individuals may experience mild side effects such as gastrointestinal discomfort, nausea, or fishy aftertaste. It’s essential to follow the recommended dosage guidelines and consult with a healthcare professional before starting any new supplement regimen, especially if you have underlying health conditions or are taking medications.
Conclusion
In conclusion, both krill oil and fish oil offer valuable sources of omega-3 fatty acids and provide a range of health benefits, including cardiovascular support, brain health, joint health, and skin health. While krill oil may have some advantages in terms of absorption and bioavailability due to its phospholipid structure, fish oil remains a popular and effective choice for omega-3 supplementation. When choosing between krill oil and fish oil, consider factors such as composition, absorption, sustainability, and personal preferences to determine which option may be the better choice for your health needs. As always, it’s essential to consult with a healthcare professional before starting any new supplement regimen to ensure safety and efficacy.
- Embark on a Cosmic Adventure: My Fun Review of Melo’s THC Beverages! - May 20, 2024
- Benefits of Black Cohosh Supplements - April 2, 2024
- Benefits of Bilberry Supplements - April 2, 2024